Peas
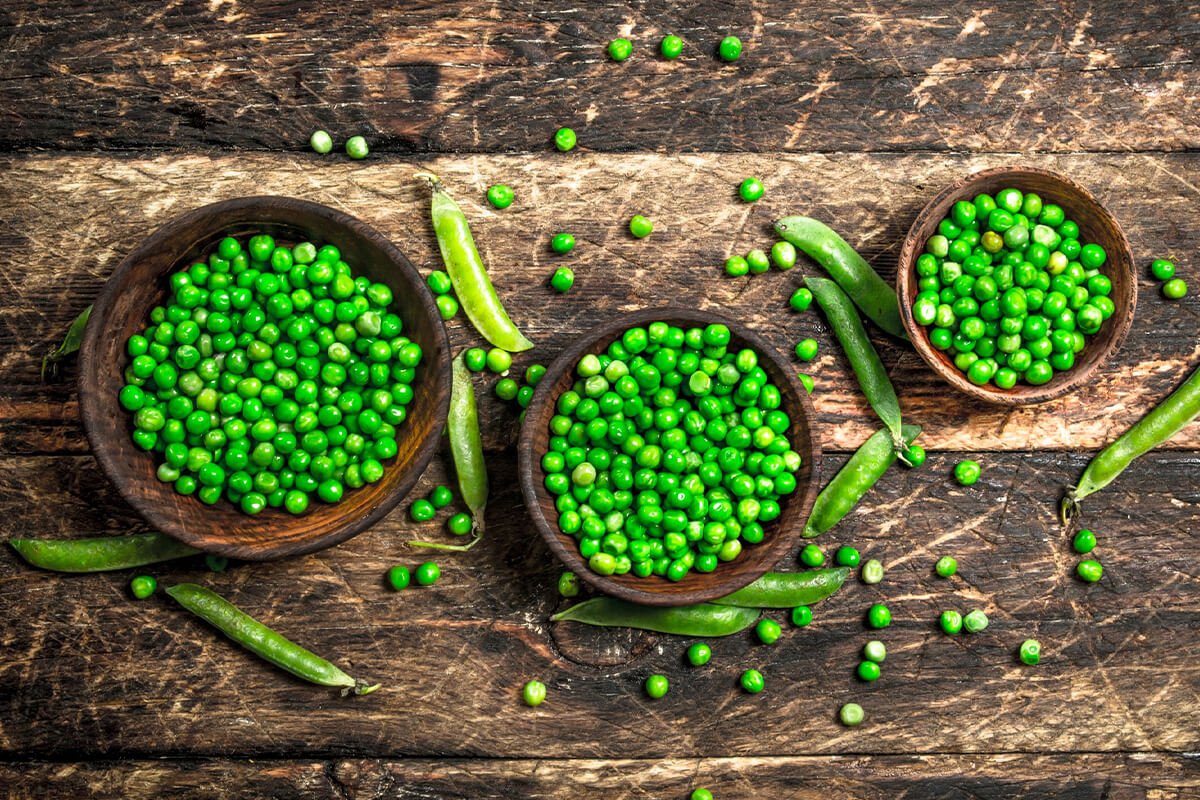

Peas
Peas thrive in cool climates and are usually planted in early spring or late fall. They prefer well-drained, fertile soil and moderate rainfall. As a legume crop, peas naturally fix nitrogen in the soil, improving fertility for future crops and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers. This makes them an eco-friendly choice in sustainable agriculture.
Peas are a high-demand export commodity due to their versatility and nutritional value. They are widely consumed in countries across Asia, Europe, North America, and the Middle East. Dried peas, especially split peas, are a staple in soups, curries, and traditional dishes worldwide. With increasing demand for plant-based proteins, peas are also used in making protein powders, snacks, and vegan alternatives, boosting their global market value.
 Calories: ~81 kcal
Calories: ~81 kcal Protein: ~5.4 g
Protein: ~5.4 g Carbohydrates: ~14 g
Carbohydrates: ~14 g Fiber: ~5 g
Fiber: ~5 g Fat: ~0.4 g
Fat: ~0.4 g
Nutritional Value (per 100g of cooked green peas)
 Protein
Protein Folate - Vitamin B9
Folate - Vitamin B9 Potassium
Potassium Fiber
Fiber Iron
Iron Manganese
Manganese Protein
Protein Folate - Vitamin B9
Folate - Vitamin B9 Potassium
Potassium Fiber
Fiber Iron
Iron Manganese
Manganese Protein
Protein Folate - Vitamin B9
Folate - Vitamin B9 Potassium
Potassium Fiber
Fiber Iron
Iron Manganese
Manganese Protein
Protein Folate - Vitamin B9
Folate - Vitamin B9 Potassium
Potassium Fiber
Fiber Iron
Iron Manganese
Manganese Protein
Protein Folate - Vitamin B9
Folate - Vitamin B9 Potassium
Potassium Fiber
Fiber Iron
Iron Manganese
Manganese Protein
Protein Folate - Vitamin B9
Folate - Vitamin B9 Potassium
Potassium Fiber
Fiber Iron
Iron Manganese
Manganese
Types of Peas
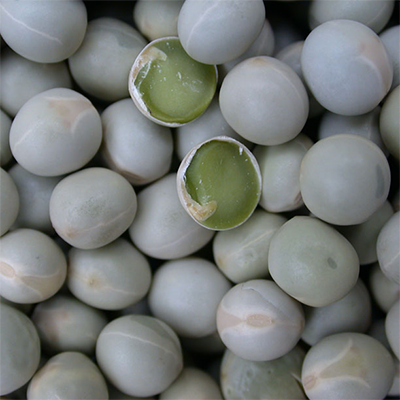

As the largest producer of the world, Canada produces mostly Green and Yellow Peas, other kinds in smaller production are maple, marrowfat and Austrian winter. Split and whole peas. Peas are excellent source of energy amino acid and protein.
As the largest producer of the world, Canada produces mostly Green and Yellow Peas, other kinds in smaller production are maple, marrowfat and Austrian winter. Split and whole peas. Peas are excellent source of energy amino acid and protein.
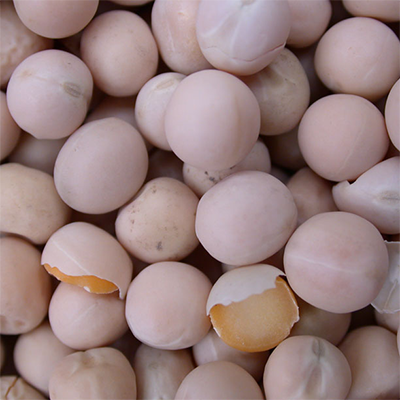

As the largest producer of the world, Canada produces mostly Green and Yellow Peas, other kinds in smaller production are maple, marrowfat and Austrian winter. Split and whole peas. Peas are excellent source of energy amino acid and protein.
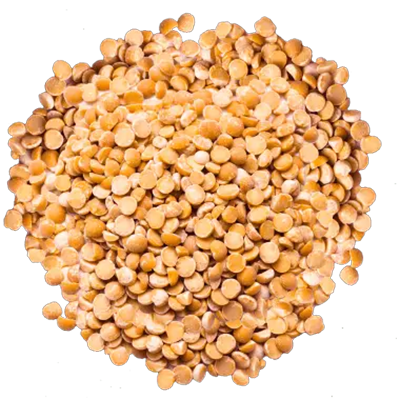

As the largest producer of the world, Canada produces mostly Green and Yellow Peas, other kinds in smaller production are maple, marrowfat and Austrian winter. Split and whole peas. Peas are excellent source of energy amino acid and protein.
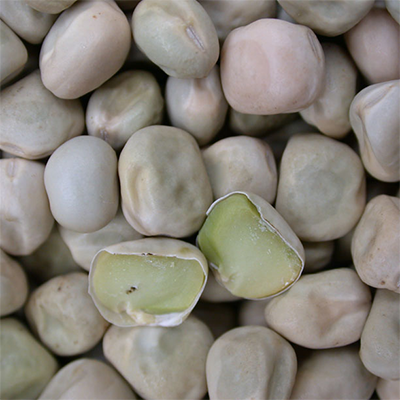

As the largest producer of the world, Canada produces mostly Green and Yellow Peas, other kinds in smaller production are maple, marrowfat and Austrian winter. Split and whole peas. Peas are excellent source of energy amino acid and protein.
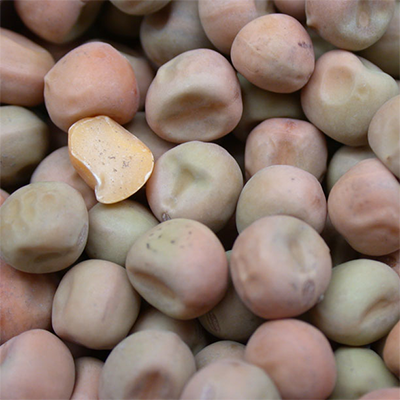

As the largest producer of the world, Canada produces mostly Green and Yellow Peas, other kinds in smaller production are maple, marrowfat and Austrian winter. Split and whole peas. Peas are excellent source of energy amino acid and protein.
We offer specialized guidance
tailored to both businesses and individuals.
Empowering Businesses through Strategic Consulting With Us
